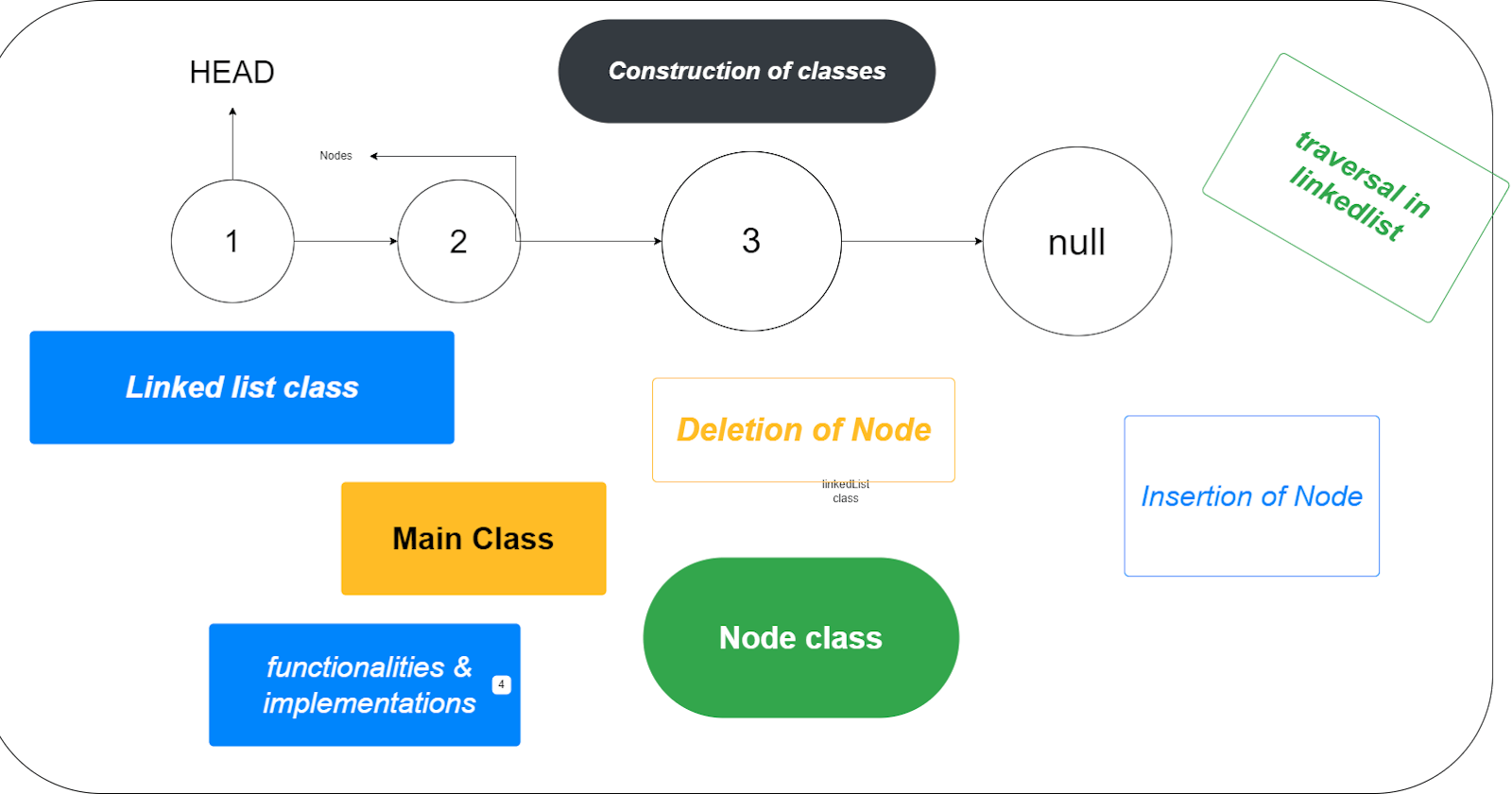
Table of contents
In order to build a linked list class, you'll typically define a structure or a class to represent the nodes of the linked list. Each node should contain two essential members:
Value: The actual data or value that the node holds.
Address (Pointer to the Next Node): A reference or pointer to the next node in the linked list.
Building Node class
// Node class represents a single node in the linked list
public class Node {
int data; /*Data or value held by the node*/
Node next; /*Reference to the next node in the linked list*/
/* Constructor to initialize a node with a given value */
public Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null; /*By default, the next node is set to null*/
}
}
Building Linked List Class
Develop a separate
linked Listclass to manage the overall structure of the linked list.Include a reference to the
headnode and a variable to keep track of the listsize.
public class linkedList {
Node head; /*Stores the first node of the linked list*/
int size; /*Stores the length of the linked list*/
public void insertNode(int data)
{
/*...............................
Implementation
.................................*/
}
public void getLength()
{
/*...............................
Implementation
.................................*/
}
public void display()
{
/*...............................
Implementation
.................................*/
}
public Node deleteNode(Node head, int position)
{
/*...............................
Implementation
.................................*/
}
}
Building Main class
Create a
Mainclass to serve as the entry point of the program.Construct a Main class and create instance of
linkedListclass in order to perform all the operations.
class Main{
public static void main(String args[])
{
linkedList list = new linkedList();
/*.....................................
perform operations : insertion, deletion, etc..
........................................*/
}
}
In the upcoming post, we will embark on an in-depth exploration of various operations and their functional implementations within the realm of linked lists.
To gain a comprehensive understanding, I encourage you to refer to our previous post, "'
RoadMap to Mastering Linked List"
For continued insights and a comprehensive journey through the intricacies of linked lists, make sure to follow the entire linked list series
"
Series on Mastering Linked List DataStructure : Linking the Dots"Stay tuned for a detailed examination of each operation, shedding light on their inner workings and practical applications.